Examples
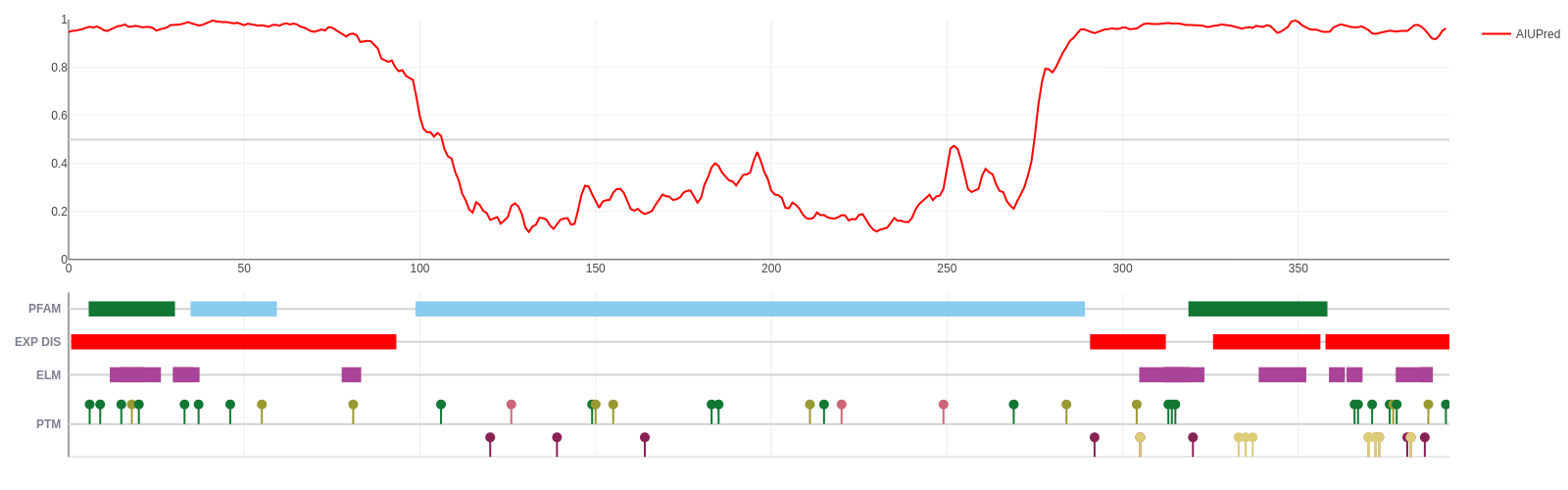
Human p53 (UniProt ID: P04637)
p53 is a tumor suppressor protein involved in apoptosis, cell cycle control and transcription regulation. It consists of the disordered N-terminal and C-terminal parts and the central largely ordered DNA binding domain.
N- and C-terminal parts contain the trans-activation and the tetramerization motifs, respectively, each with its own Pfam motif. The structure of the central DNA binding domain (DBD) was determined both in isolation and bound to DNA as well. However, the disordered regions also incorporate a large number of solved structures from the PDB, but since these regions do not have a stable structure on their own, their structures can only be determined when bound to some molecular partner.
The disorder prediction score in red correctly highlights the ordered nature of the DBD and the disordered nature of both termini. Both the N- and the C-terminal binding motifs display reduced disorder tendency, which is a characteristic feature of protein-interacting disordered binding sites.
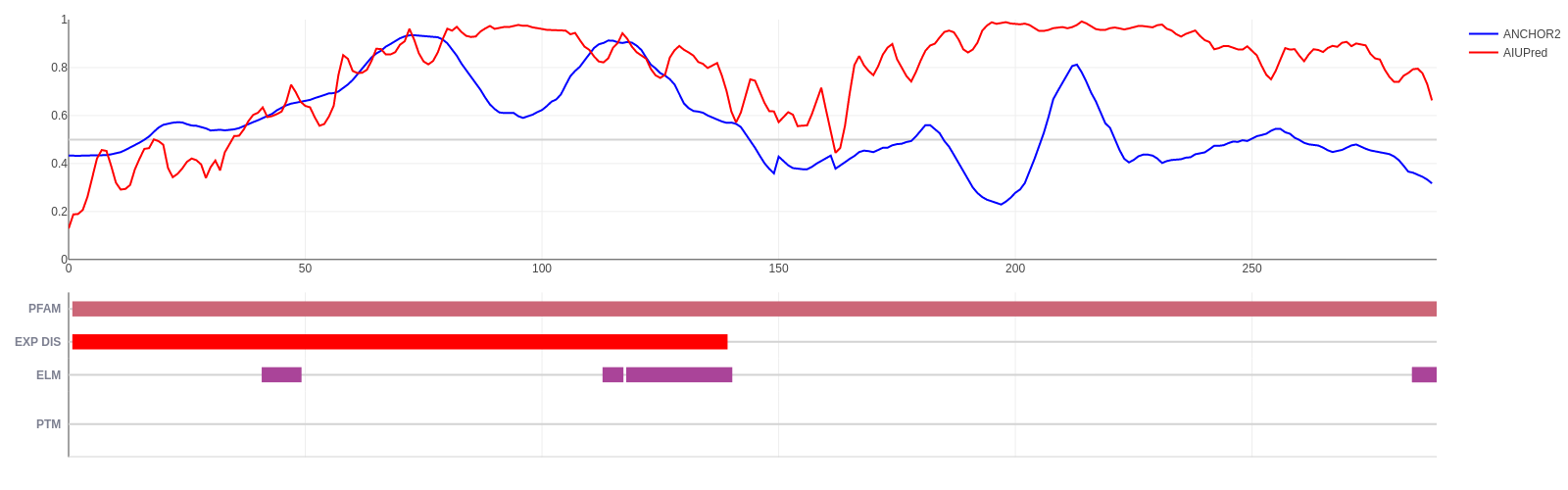
Early E1A protein (UniProt ID: P03255)
Human adenovirus C early E1A protein is a largely disordered protein essential for forcing the human host cell into S phase via modulation of the Rb1/E2F1 pathway and the inhibition of apoptosis via modulation of p53 degradation. These host-pathogen interactions are mediated by several binding events. Rb1 and CBP are targeted by two N-terminal tandem binding sites with determined complex structures deposited in the PDB, shown in green and red boxes. These known disordered binding regions are identified by ANCHOR2 as two distinct neighbouring peaks in the output score. While no other E1A- human protein complexes are currently known in structural detail, E1A harbors two additional known motifs between residues 113-126 capable of forming host-specific interactions. Both motifs, together with the putative binding site for the deubiquitinase UBE2I between residues 76-140 are correctly recognized by ANCHOR2 as a separate peak in the prediction score. A distinct peak C-terminal around residue 220 has no known binding partners; however it entails a serine residue that was shown to be heavily phosphorylated by host kinases, hinting at an additional important binding region with currently limited characterization.
Gábor Erdős, Zsuzsanna Dosztányi
Nucleic Acids Research 2024; gkae385
AIUPred – Binding: Energy Embedding to Identify Disordered Binding Regions
Gábor Erdős, Norbert Deutsch, Zsuzsanna Dosztányi
Journal of Molecular Biology 2025
